NFT Royalty Battle Royale
How Martketplaces are battling for market share using creator royalties as the lever.
The NFT ecosystem has debated the best approach to NFT royalties since the inception of NFT marketplaces. Recently, this debate has become heated and is at the center of big marketplace competition, primarily the battle between OpenSea and Blur. However, this debate is a crucial topic for the future success of NFTs, with royalties being one of their most important and revolutionary pieces of functionality. But before we dive into the specifics of the royalty stand-off between marketplaces, let's cover the basics.
What are NFT royalties?
NFT royalties are a percentage of the sale price paid to the creator every time the NFT is sold to a new owner. This means that the creator of an NFT can continue to earn money even after the initial sale. NFT royalties are designed to protect the intellectual property rights of creators and ensure that they are fairly compensated for their work.
Why are NFT royalties important?
NFT royalties are important because they allow creators to earn a steady income from their work. In the traditional art world, artists often only receive payment for their work once, and then the artwork can be resold for much higher prices without the artist receiving any additional compensation. NFT royalties help to ensure that creators are compensated fairly and can continue to earn money from their work even after it has been sold. Because an NFT has the potential to represent ownership over many types of assets, far beyond basic artwork (music, game items, deeds, etc.), NFT royalties are a novel way to provide compensation in perpetuity for creators of all types.
How do NFT royalties work?
When an NFT is created, the creator can set a royalty percentage they will receive every time the NFT is sold. This percentage is usually around 1-5%, but it can be as high as 50%, depending on the creator's preferences. Once the NFT is sold, the royalty percentage is automatically paid out to the creator's wallet.
There are three types of mechanisms for royalties:
Marketplace Enforced
Royalties are enforced at the marketplace level. This is typically accomplished by encoding logic into the marketplace smart contract that enables the transfer of assets and value from one party to another. In an effort to standardize royalties across marketplaces manifold.xyz created an on-chain registry in collaboration with many of the major marketplaces that can be relied on to determine the royalties configuration of any given NFT. You can learn more about this registry at royaltyregistry.xyz.
In an attempt to incentivize the enforcement of royalties for all marketplaces, both OpenSea and Blur also recently launched an open-source blacklist registry that can be implemented by NFT smart contract creators. The registry provides creators with a mechanism to prevent the support of marketplaces that do not support creator royalties.
OpenSea’s Registry
https://github.com/ProjectOpenSea/operator-filter-registry
Blur’s Registry
https://github.com/blur-io/operator-filter-registry
Contract Optional
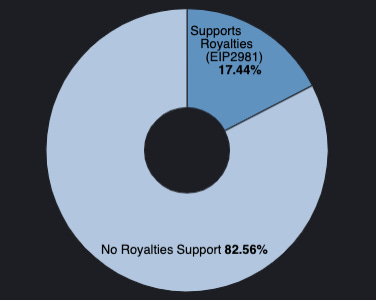
Royalties are not enforced, but instead, standards are implemented at the NFT contract level to suggest to marketplaces how to handle royalties for a specific NFT. The primary interface used to implement this functionality is EIP 2981. Implementing EIP 2981 has gained support since its inception. According to our data, approximately 17.44% of all collections have implemented the Royalties standard.
Contract Enforced
Royalties are enforced at the contract level. In order for this to be possible, each NFT contract must implement marketplace functionality. EIP 6105 describes a standard to enable “intermediary-free NFT trading,” which would enable trading without reliance on a marketplace contract. However, this standard is still unable to prevent trading NFTs on marketplaces that bypass the built-in trading mechanics and would need to implement a blacklist similar to the above Operator Filter Registry.
Blur vs. OpenSea
On Nov 5th 2022, OpenSea announced a change to their royalties mechanics. The goal of the change was to provide a mechanism to enforce on-chain royalties through a blacklist registry contract (the aforementioned Operator Filter Registry). One downside to this approach was that contracts that do not implement the new standard would no longer receive royalties at all. This change was both celebrated and criticized.
On one hand, moving closer toward an NFT ecosystem with enforced royalties is good for creators by ensuring their royalties are respected. On the other hand, by blacklisting marketplaces, OpenSea has introduced an anti-competitive mechanism that restricts the free market nature of NFT trading.
Read their original Twitter thread: OpenSea on Twitter
On Nov 14, 2022 Marketplace Blur announced its strategy for royalties. In an effort to both win market share and incentivize royalties to be paid, Blur created its own version of the Operator Filter Registry that allows creators to enforce and earn royalties on both Opensea and Blur, bypassing OpenSea’s version of the registry. In addition to the new Registry, Blur attempts to incentivize paying collection royalties through the use of the $BLUR rewards token. Somewhat ironically, Blur provides larger rewards to traders who exclusively trade on Blur (e.g. do not have any orders open on any other marketplace).
Read their original Twitter thread: Blur on Twitter
For the time being, Blur's strategy has increased creator royalties due to the benefits of farming the $BLUR token. However, it's unclear what the longevity of this mechanism looks like and whether or not Blur will maintain this competitive advantage.
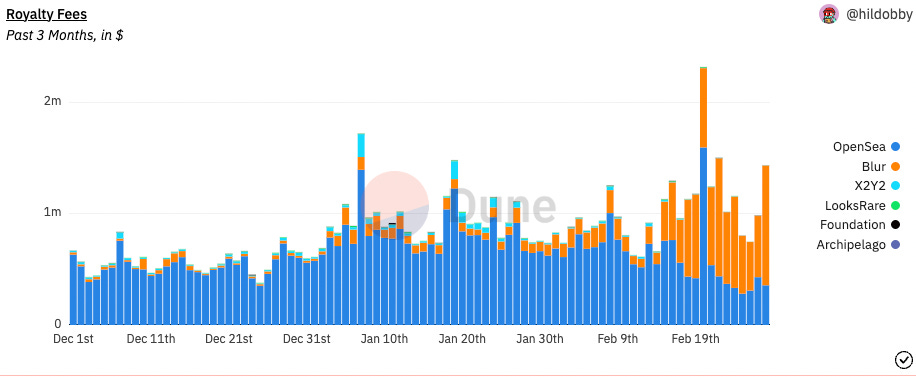
The following Dune Analytics dashboard offers an in-depth view of Royalties analytics:
https://dune.com/hildobby/nft-fees
Creators vs. Marketplaces
While the intentions behind OpenSea and Blurs strategies might be good, the reality is that it is also opportunistic. Marketplaces have the incentive to increase their market share and bottom line. So, what's really happening? OpenSea and Blur are duking it out. The primary objective for both is to maintain (in Blur's case, win more) market share. Unfortunately, there is no perfect option. Enforcing royalties causes traders to flee to cheaper marketplaces, not enforcing royalties will still inevitably lead to a race to the bottom, as most NFT buyers are traders looking to make a profit.
Ultimately, the CR3 Labs team is aligned with creators, but we understand the complexities of royalty enforcement both from a technical and a business model perspective. Royalties are a fundamental mechanism that makes NFTs revolutionary and useful. Creators have the right to decide if they will enforce royalties, and marketplaces/buyers should not. The levers that should be pulled for marketplace competition should be marketplace fees, incentive/reward mechanisms, and novel innovation, not creator royalties. Unfortunately, this is only in a perfect world - aligning all creators and platforms on the use of NFT smart contracts with enforced royalties is unlikely to happen soon.
“If royalties are increasingly ignored by market participants, we think it could threaten the adoption of the technology more broadly.
- Coinbase
Marketplace Royalties & Fees
Royalty: Enforced for most new collections
Fee: 0% (temporarily waved for collections with high volume )
Blur:
Royalties: Enforced for new collections, Royalty incentives via $BLUR
Fee: 0%
Royalties: Optional
Fee: 2% (1.5% to LOOKS stakers, 0.5% to Creators as an enforced royalty)
X2Y2:
Royalties: Enforced
Fee: 0.5%
Notable mentions
Magic Eden: Optional royalties (opt-in like a tip)
PsudoSwap: No creator royalties
Magically: zero royalty fees
GonnaMakeIt: User protection, Royalty protection
About CR3 Labs
CR3 Labs builds tooling for Web3 gaming to help creators, collectors, and gamers unlock value in the new digital frontier.
Learn more at https://www.cr3labs.com.
Seeking more information about a particular topic, project, or technology?
Submit a research request!